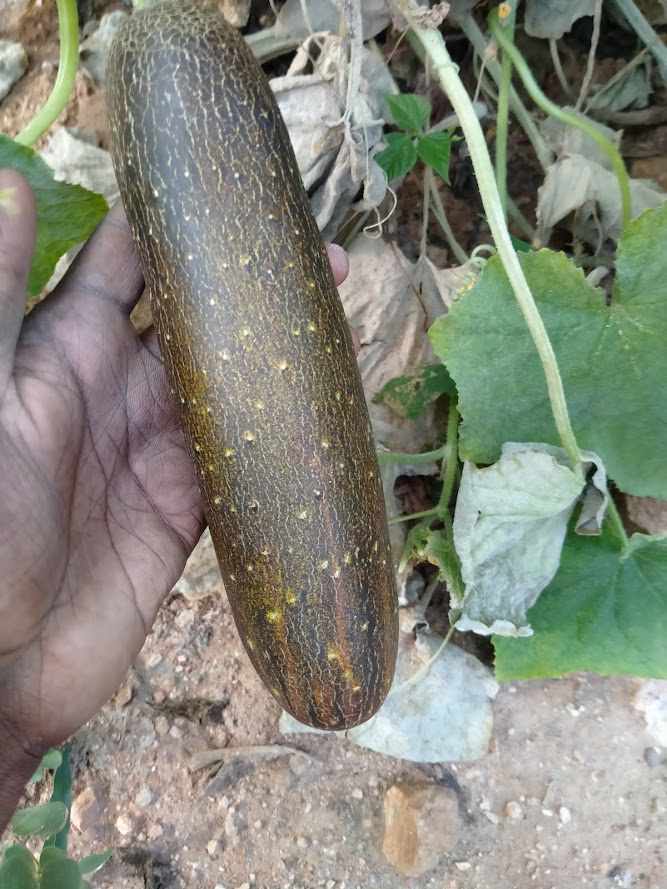
Poona kheera cucumbers produce large fruits which are traditionally cut into slices for use in salads and as a garnish. They are a fast growing crop under good growing conditions. The maturity is between 55 to 65 days. Poona kheera cucumber is grown in spring and summer. Usually, cucumber plants can't withstand frost at all. So, plant in hot and warm conditions.
Cucumbers are native to the tropics and absolutely must have warm soil (70˚ F minimum) for good germination and growth. Consequently they are among the last crops to be planted out in spring. Most varieties fruit better in short days, so they tend to be more productive later in the summer. Cucumbers take 2 weeks to germinate at 60 degrees, but only 3 days at 85 degrees. Cucumbers can be grown in partial shade. I.e it needs atleast 6 hours of full sun light.
The best way to water Cucumbers is with a drip system or soaker hose, as this keeps the leaves dry and so reduces the chance of disease problems. If you must get the leaves wet, water in the morning, or early evening, so they have a chance to dry out quickly. You don't want the leaves to stay wet all night.
Be careful not to overwater germinating seeds or they may rot. It's best to soak the ground or the potting soil heavily when first planting, then avoid watering again if possible until seedlings emerge. Cucumber seeds emerge in 5+ days; very lightly water ground or potting soil around day 3 or 4 to keep soil from crusting so that seeds can emerge more easily.
Poona kheera Cucumbers grow quite well in containers and several varieties have been produced specifically for this. They will be more productive in larger containers (at least 12" in diameter). In order to prevent root rot, it is important that your container has drainage holes. Line the bottom of your container with weed cloth or newspaper and then cover with a handful of small rocks. Fill the remainder with amixture of peat moss, compost and potting soil. Cucumbers need a minimum of 6 hours of sunlight per day. In extremely hot climates, it is best to provide partial shade and keep your container away from direct sunlight. Cucumbers need lots of water, and they prefer moist soil.
Poona kheera cucumbers attracts beneficial insects. The fruit size of the cucumber is 6 inches to 11 inches. The fruits on maturing will turn to brown from green. So, harvest the fruits while it is still green.