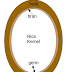
The Food forests are also called as Regenerative farming or no till farming. Here you no need to till the land for cropping. Nature does it all.
This article is continued from the last post. Where we were discussing on how to create Indian food forests part I fruit trees etc...
There are other fruit trees which are native and grow well in Indian climate conditions. They are given below.
Pomegranate Tree
Pomegranate is a small tree cultivated throughout the Middle East and India. A shrub also grown as ornamental trees in some parks and gardens.
Jamun/Syzygium cumini
This tree is commonly called jamun in India. Syzygium cumini is native to the Indian Subcontinent, known as black plum or jamun. The fruit tends to colour the tongue purple with its sweet, mildly sour flavor.
Gooseberry Tree/Phyllanthus acidus
Phyllanthus acidus or Gooseberry tree with edible small yellow berries fruit tastes sour and tart. The plant is also used medicinally in India and produces fruit throughout the year. The first image is Indian gooseberry tree which has medicinal properties to cure few diseases.
Coconut Tree/Cocos nucifera
Coconut Tree is a Plant growing up to 30 m, originated in the India–Indonesia region. Coconut palms are grown around the world, India is third largest producer of Coconut in the world, cultivation states of India are the of Kerala, Tamil Nadu, Karnataka to Lakshadweep.
Indian Jujube/Ziziphus mauritiana/ ber tree
Indian jujube or Indian plum is a tropical fruit tree from the Indian Subcontinent. Ziziphus mauritiana are wild growing plants as well as common trees of semi arid regions of India.
Jungli Jalebi/Pithecellobium dulce
Jungli Jalebi is an invasive species and a drought resistant tree. Pithecellobium dulce goes by the name Madras thorn in India and used in medicine too.
Indian Fig Tree/Ficus racemosa
Ficus racemosa or cluster fig tree is native to Indian subcontinent and favourite food of the Indian macaque. Indian fig or gular is also known as audumbar tree,both sacred and fruitful.
Cashew Tree/Anacardium occidentale
Anacardium occidentale is large and evergreen tree and fruit is called cashew apple and cashew nut inside. The cashew tree is native to Brazil and Portuguese took it to Goa in India.
Indian Almond/Terminalia catappa
Terminalia catappa tree is grown as an ornamental tree for shade and wild fruit. The large leaves and distinctively arranged branches of Terminalia catappa are evergreen tree.
Mulberry Plant/Morus
Morus Plant or mulberry tree is a fast growing tree and the fruit is edible too. The fruit and leaves contains significant amounts of resveratrol.
These are the some of the fruit trees for your food forest. The perennial vegetables you can choose according. We would like to post few vegetables which are perrineals that are suited for the food forests. Stay tuned...!
Upcoming article : How to create Indian food forest Part III Perrineals
To keep updated follow us. Visit our sitemap page which contains all our articles.
#almond #coconut #mulberry #cashew #indianfigtree #pomegranate #gooseberry #junglejalebi
This article is continued from the last post. Where we were discussing on how to create Indian food forests part I fruit trees etc...
There are other fruit trees which are native and grow well in Indian climate conditions. They are given below.
Pomegranate Tree
Pomegranate is a small tree cultivated throughout the Middle East and India. A shrub also grown as ornamental trees in some parks and gardens.
Jamun/Syzygium cumini
This tree is commonly called jamun in India. Syzygium cumini is native to the Indian Subcontinent, known as black plum or jamun. The fruit tends to colour the tongue purple with its sweet, mildly sour flavor.
Gooseberry Tree/Phyllanthus acidus
Phyllanthus acidus or Gooseberry tree with edible small yellow berries fruit tastes sour and tart. The plant is also used medicinally in India and produces fruit throughout the year. The first image is Indian gooseberry tree which has medicinal properties to cure few diseases.
Coconut Tree/Cocos nucifera
Coconut Tree is a Plant growing up to 30 m, originated in the India–Indonesia region. Coconut palms are grown around the world, India is third largest producer of Coconut in the world, cultivation states of India are the of Kerala, Tamil Nadu, Karnataka to Lakshadweep.
Indian Jujube/Ziziphus mauritiana/ ber tree
Indian jujube or Indian plum is a tropical fruit tree from the Indian Subcontinent. Ziziphus mauritiana are wild growing plants as well as common trees of semi arid regions of India.
Jungli Jalebi/Pithecellobium dulce
Jungli Jalebi is an invasive species and a drought resistant tree. Pithecellobium dulce goes by the name Madras thorn in India and used in medicine too.
Indian Fig Tree/Ficus racemosa
Ficus racemosa or cluster fig tree is native to Indian subcontinent and favourite food of the Indian macaque. Indian fig or gular is also known as audumbar tree,both sacred and fruitful.
Cashew Tree/Anacardium occidentale
Anacardium occidentale is large and evergreen tree and fruit is called cashew apple and cashew nut inside. The cashew tree is native to Brazil and Portuguese took it to Goa in India.
Indian Almond/Terminalia catappa
Terminalia catappa tree is grown as an ornamental tree for shade and wild fruit. The large leaves and distinctively arranged branches of Terminalia catappa are evergreen tree.
Mulberry Plant/Morus
Morus Plant or mulberry tree is a fast growing tree and the fruit is edible too. The fruit and leaves contains significant amounts of resveratrol.
These are the some of the fruit trees for your food forest. The perennial vegetables you can choose according. We would like to post few vegetables which are perrineals that are suited for the food forests. Stay tuned...!
Upcoming article : How to create Indian food forest Part III Perrineals
To keep updated follow us. Visit our sitemap page which contains all our articles.